Rediscovery of Hydrogen: The Clean Fuel Revolutionizing The Automotive Industry
Imagine a world where vehicles emit nothing more than water vapor as they speed down highways. No, this isn't a scene from a science fiction movie but rather a potential reality with the rise of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles. In this article, we delve into the history, current trends, and impacts of this promising technology in the automotive industry.
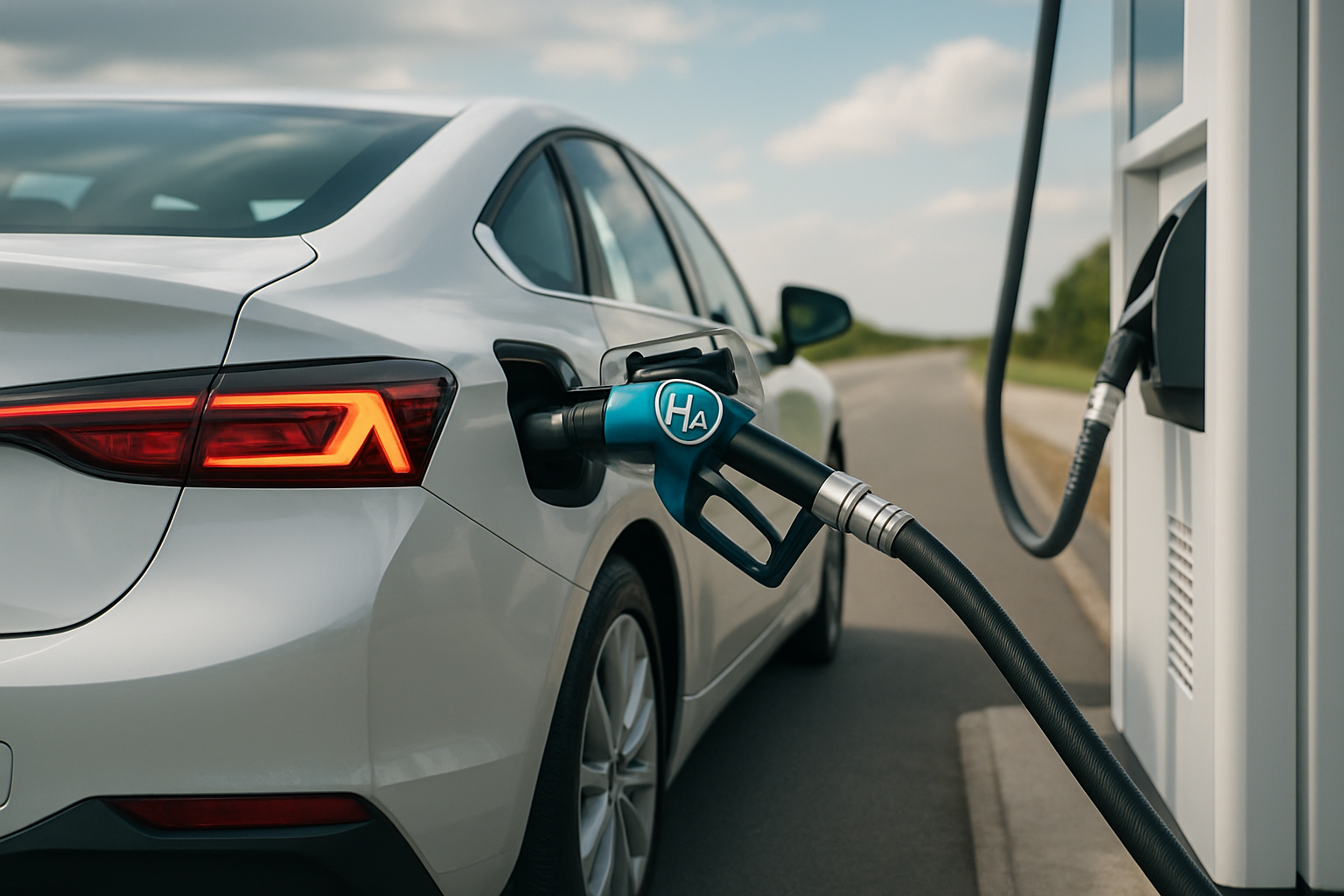

The Origins and Progression of Hydrogen Fuel Cell Technology
Hydrogen fuel cell technology isn’t new. In fact, its origins can be traced back to 1839, when British scientist Sir William Grove discovered the principle of water electrolysis. However, it wasn’t until the 1960s that this technology began to be seriously considered for powering vehicles, with General Motors developing the first hydrogen fuel cell vehicle prototype, the GM Electrovan.
Despite the technology’s early promise, it was largely overshadowed by internal combustion engines due to several challenges. Hydrogen storage and production were expensive and inefficient, and the lack of a refuelling infrastructure made hydrogen cars less practical than their gasoline counterparts.
Fast forward to today, and advancements in technology have made hydrogen fuel cells more efficient, less costly, and safer. Modern fuel cell vehicles, like Toyota’s Mirai and Hyundai’s NEXO, are capable of matching conventional cars in terms of range and refuelling time, making them a viable alternative to gasoline and even electric vehicles.
Riding the Wave of Current Trends
As the world grapples with climate change and the need to reduce carbon emissions, hydrogen fuel cell vehicles are gaining renewed interest. Governments and automakers are increasingly investing in hydrogen technology and infrastructure. For instance, Japan has set a target of having 800,000 fuel cell vehicles on its roads by 2030, supported by a network of 900 hydrogen refuelling stations.
Moreover, the versatility of hydrogen fuel cells is seeing them being utilized beyond passenger cars. They’re making their way into commercial trucks, buses, and even trains and ships, offering a broader scope for reducing transport-related emissions.
Balancing the Scales: The Impact, Advantages, and Challenges
Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles offer numerous benefits. They produce zero tailpipe emissions, their high energy density provides a long driving range, and they can be refueled in minutes, addressing some of the key limitations of electric vehicles.
However, there are still challenges to overcome. Hydrogen production is currently heavily reliant on natural gas, thus negating some of its environmental benefits. Additionally, the lack of widespread refuelling infrastructure and high vehicle costs compared to conventional and electric cars are barriers to mass adoption.
The Road Ahead: Fuelling the Future
Despite the challenges, the future of hydrogen fuel cell technology in the automotive industry looks promising. With continued research and development, advancements in green hydrogen production, and government and industry commitments to building infrastructure, hydrogen cars could play a significant role in the transition to a decarbonized transport sector.
In conclusion, the rediscovery of hydrogen as a clean, efficient energy source holds great potential for revolutionizing the automotive industry. The journey may be long and fraught with challenges, but the destination—a sustainable and emission-free transportation future—is undoubtedly worth it.