Understanding Modern Network Infrastructure
Modern network infrastructure forms the backbone of our interconnected world, enabling seamless digital communication and data exchange across vast distances. From the simple act of browsing the internet to complex global operations, this intricate system of hardware, software, and protocols ensures that information flows efficiently and reliably. Exploring its fundamental components and operational principles provides insight into how our contemporary society functions in an increasingly digital landscape, highlighting the continuous evolution required to meet growing demands for speed and accessibility.
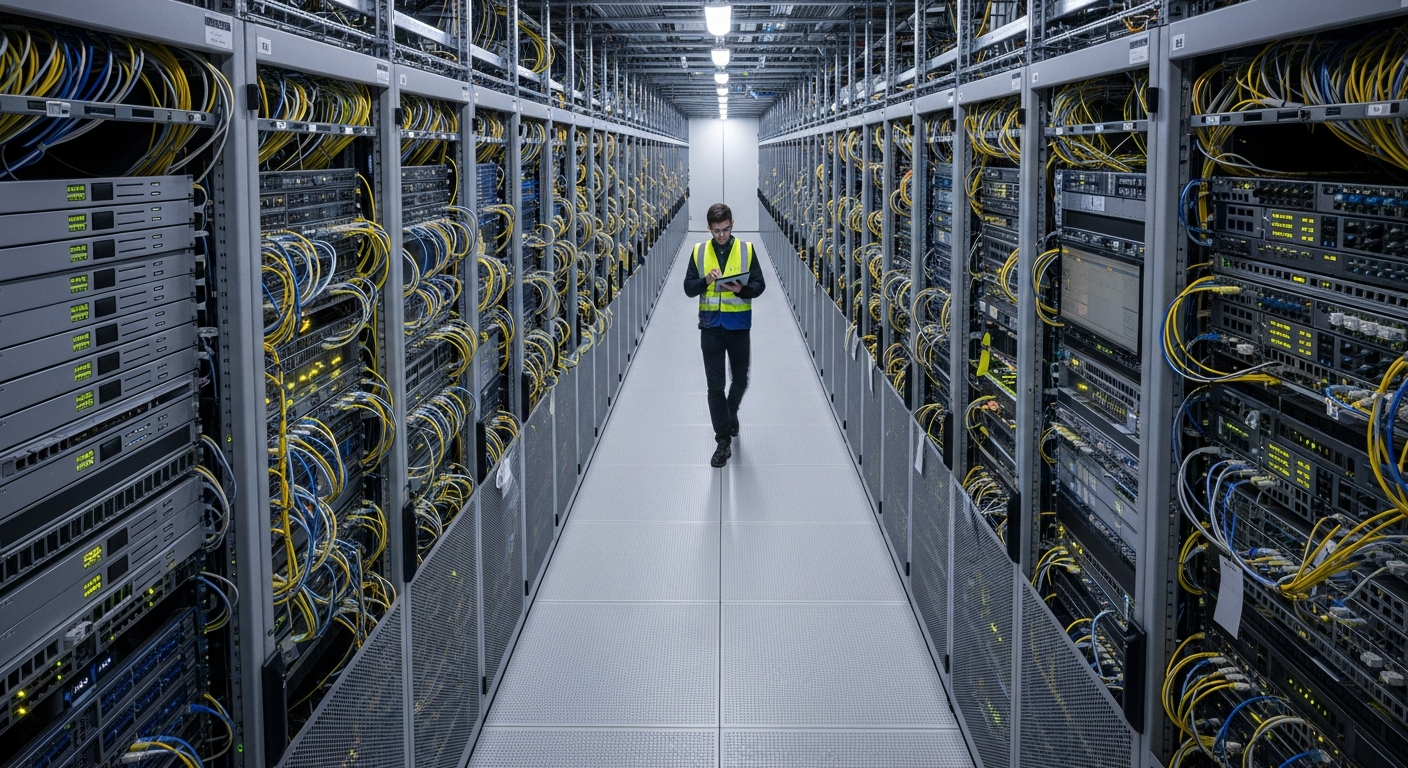

The Core Components of Network Connectivity
Modern network infrastructure is a complex ecosystem designed to facilitate global connectivity. At its heart are various interconnected networks, ranging from small local area networks (LANs) to wide area networks (WANs) that span continents. These digital pathways rely on a combination of physical and virtual elements. Physical infrastructure includes cables, routers, switches, and data centers, which are essential for directing traffic and storing information. Logically, protocols like TCP/IP govern how data is formatted, addressed, transmitted, and received, ensuring that diverse devices can communicate effectively. This foundation is critical for everything from personal messaging to large-scale industrial operations.
Advancements in Broadband and Wireless Communication
Significant strides in broadband and wireless communication have revolutionized how individuals and organizations connect. Broadband technologies, such as DSL, cable, and fiber optics, offer high-speed internet access, supporting bandwidth-intensive applications like video streaming and cloud computing. Simultaneously, wireless technologies, including Wi-Fi, 4G, and 5G, have provided unprecedented mobility and flexibility, allowing devices to stay connected without physical cables. The continuous development in these areas focuses on increasing speed, reducing latency, and expanding coverage, pushing the boundaries of what is possible in real-time data exchange and remote operations.
The Role of Fiber Optics and Satellite Technology
Fiber optics stands as a cornerstone of high-performance infrastructure, transmitting data as pulses of light through thin glass strands. This technology offers superior bandwidth and significantly lower signal loss over long distances compared to traditional copper cables, making it ideal for national and international backbones. Complementing terrestrial fiber, satellites play a vital role in extending access to remote or underserved areas, providing connectivity where ground-based infrastructure is impractical or impossible. Geostationary and low Earth orbit (LEO) satellite constellations are continuously being deployed to enhance global coverage and reduce latency for satellite-based internet services, bridging digital divides and supporting critical communication needs worldwide.
Ensuring Data Speed, Access, and Security
For any network infrastructure, ensuring optimal data speed and ubiquitous access is paramount. Network architects continuously work to optimize routing paths, increase bandwidth capacity, and implement caching mechanisms to deliver content quickly to end-users. Beyond speed, the security of network infrastructure is a critical concern. With the increasing volume and sensitivity of data transmitted, robust cybersecurity measures are essential to protect against cyber threats, data breaches, and unauthorized access. This involves implementing firewalls, intrusion detection systems, encryption protocols, and regular security audits to maintain the integrity and confidentiality of information across all points of the network. These efforts ensure trust and reliability in the digital ecosystem.
Future Trends in Global Network Innovation
The future of network infrastructure is characterized by relentless innovation aimed at even greater global connectivity. Emerging trends include the deployment of 5G and future-generation wireless standards, which promise ultra-low latency and massive device connectivity for applications like the Internet of Things (IoT) and autonomous systems. The efficient management of spectrum resources is crucial for these advancements. Furthermore, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) is enhancing network management, enabling predictive maintenance, automated anomaly detection, and dynamic resource allocation. These developments are paving the way for more intelligent, resilient, and responsive networks that can adapt to ever-changing demands and support the next wave of digital transformation.
Modern network infrastructure is an intricate and continuously evolving system that underpins almost every aspect of contemporary life. From the foundational cables and wireless signals to advanced satellite technology and sophisticated security protocols, each component plays a crucial role in facilitating global communication and data exchange. The ongoing pursuit of greater speed, broader access, and enhanced security drives constant innovation, ensuring that the digital world remains connected and responsive to the needs of a rapidly advancing society.