Recycling Innovations for Electronic Waste
The rapid advancement of technology has led to an unprecedented increase in electronic waste, commonly known as e-waste, presenting significant environmental challenges. As consumers and industries embrace new digital devices and systems, the discarded electronics accumulate, often containing hazardous materials alongside valuable resources. Addressing this growing concern requires innovative approaches to recycling, moving beyond traditional methods to recover more materials efficiently and sustainably. Exploring these advancements is crucial for fostering a circular economy and mitigating the ecological footprint of our digital age.

The proliferation of electronic devices across the globe has brought immense convenience and progress, yet it also presents a formidable challenge: managing the escalating volume of electronic waste. From smartphones to complex computing hardware, these items often contain precious metals and rare earth elements, alongside potentially harmful substances. Traditional recycling methods, while beneficial, can sometimes fall short in efficiently recovering all valuable components or safely neutralizing hazardous materials. This reality underscores the urgent need for continuous innovation in how we approach electronic recycling.
Enhancing Electronic Waste Recycling Processes
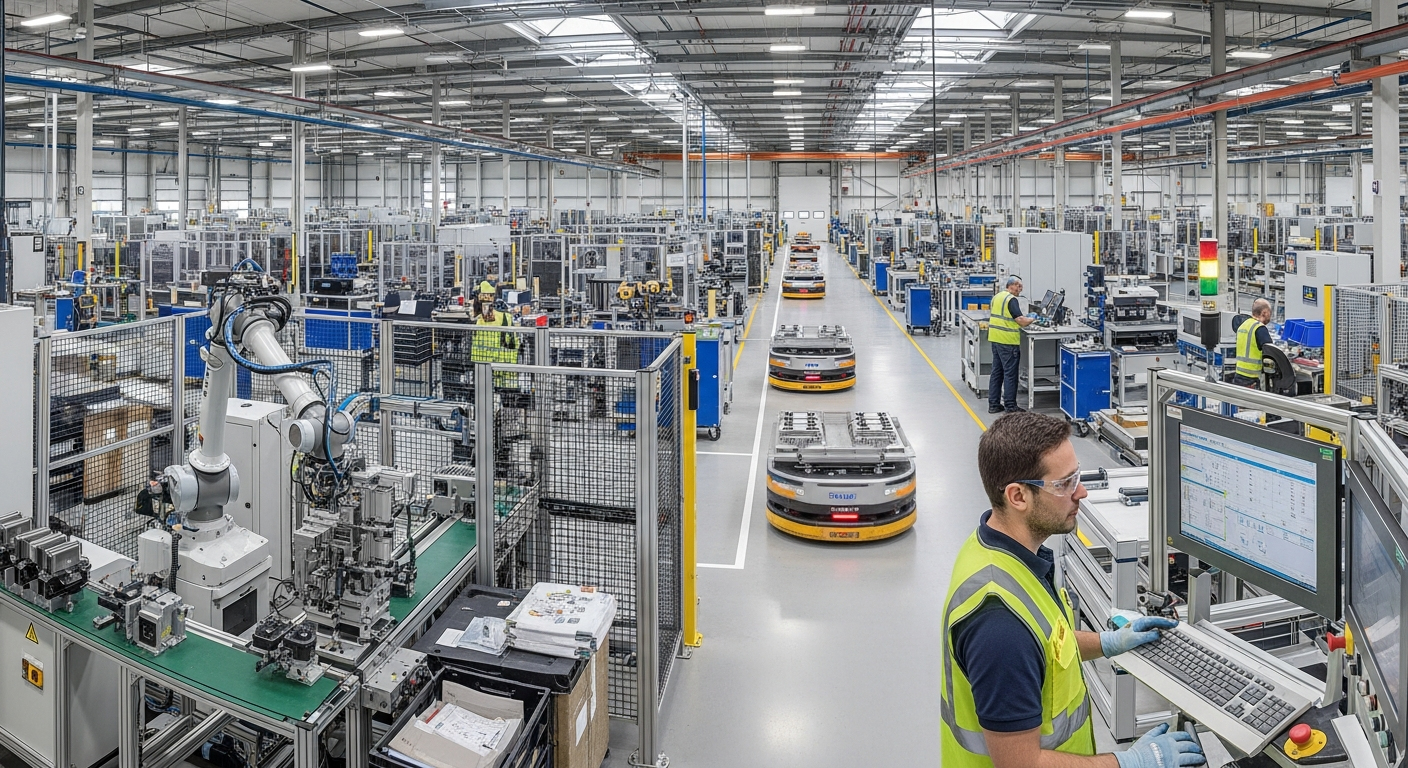
Innovation in recycling processes is critical for improving the efficiency and environmental impact of e-waste management. Modern recycling facilities are increasingly adopting advanced mechanical and chemical processes to separate materials more effectively. These methods aim to extract high-purity raw materials, such as copper, gold, silver, and palladium, from discarded electronic components. The goal is not just to reduce landfill waste but also to minimize the need for virgin material extraction, thereby conserving natural resources and reducing the energy consumption associated with mining and refining.
Role of Advanced Technology in Component Recovery
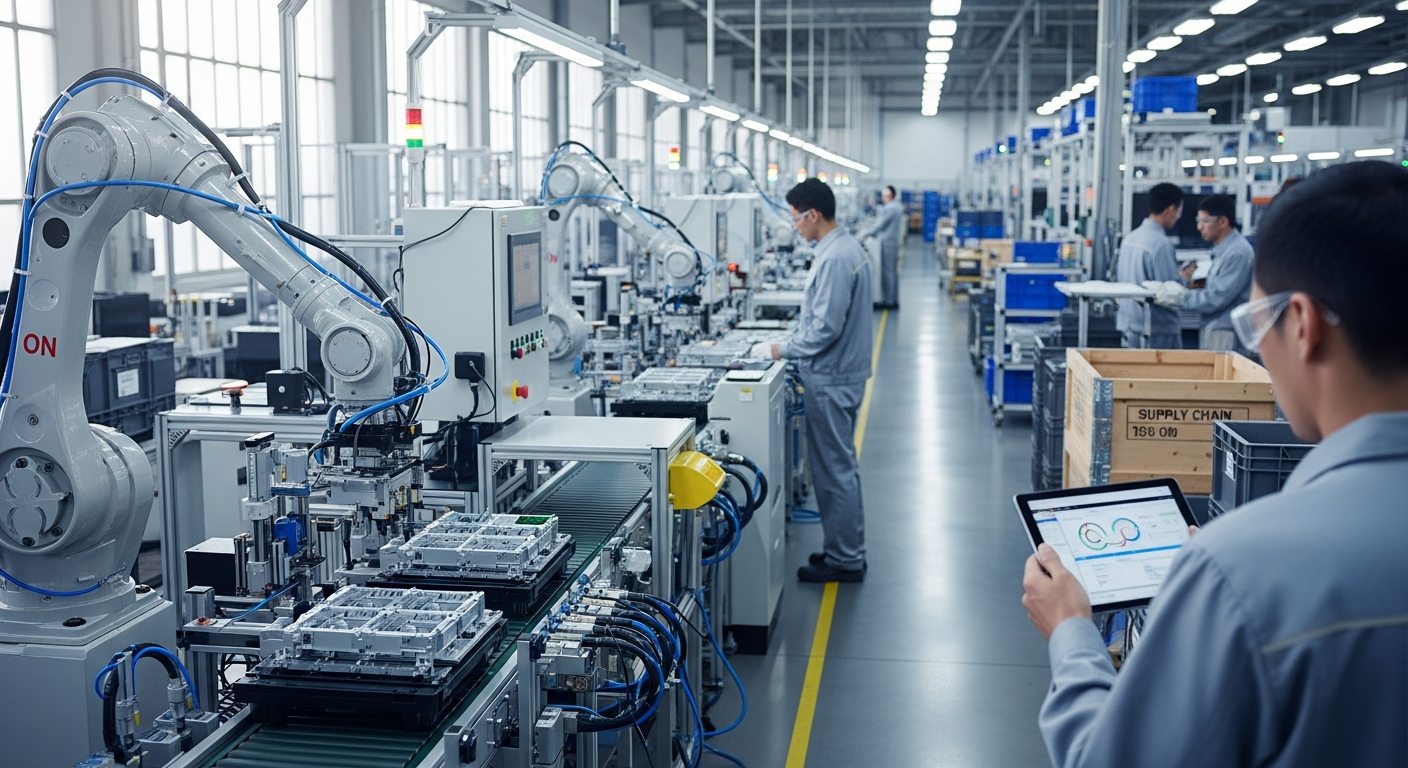
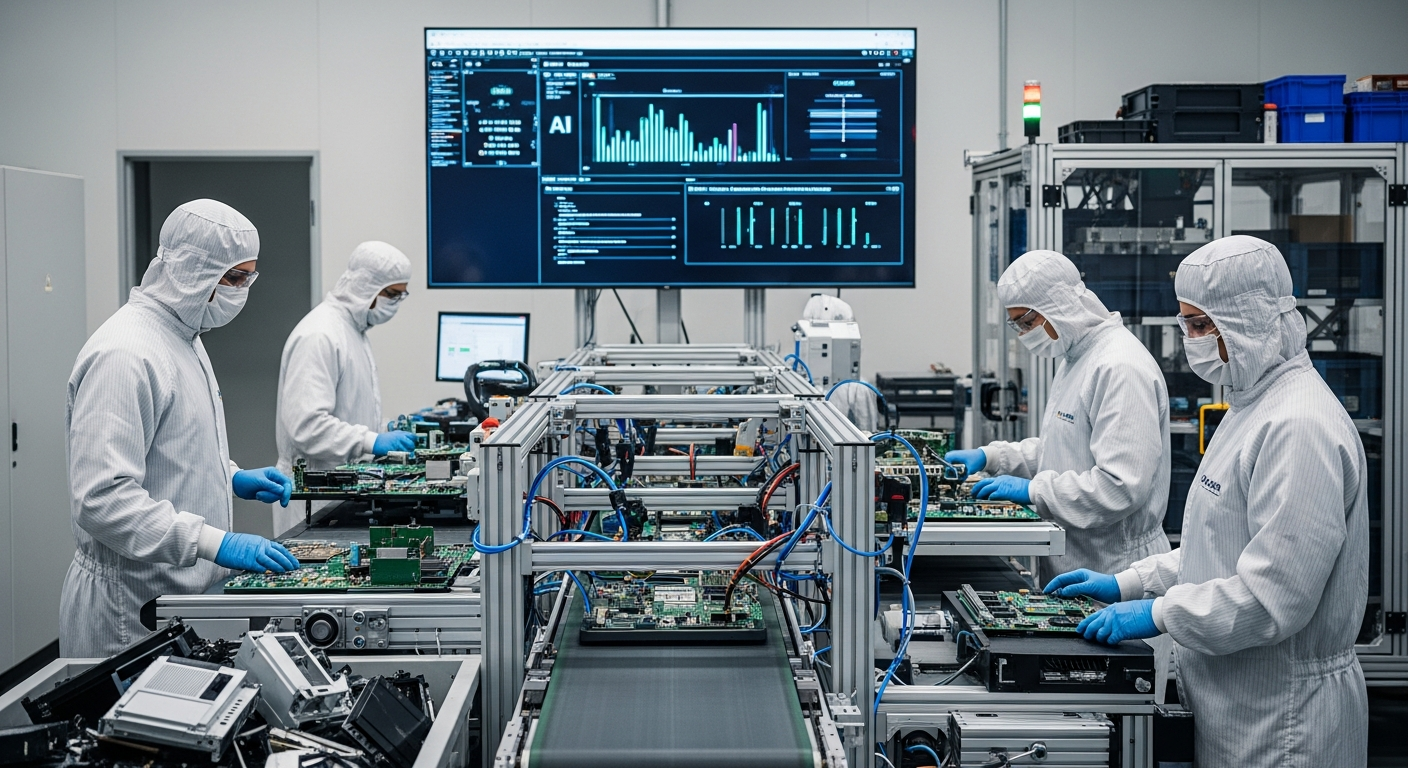
Advanced technology plays a pivotal role in maximizing the recovery of valuable components from electronic devices. Techniques like artificial intelligence (AI) and robotics are being integrated into sorting lines to identify and separate different types of plastics, metals, and circuit boards with greater precision and speed than manual methods. Specialized shredding and separation technologies can break down complex assemblies into constituent materials, making it easier to isolate specific elements. This technological integration is crucial for processing the diverse and ever-evolving array of electronic hardware and digital systems entering the waste stream.
Nanotech and Sensors in E-waste Sorting
Emerging fields like nanotechnology and advanced sensor technologies are offering promising solutions for e-waste management. Nanotech applications could potentially enable the development of more efficient chemical processes for extracting trace amounts of rare metals or for neutralizing toxic substances at a molecular level. Meanwhile, sophisticated sensors can be deployed to accurately detect and differentiate materials, even those present in small quantities, enhancing the precision of automated sorting systems. These innovations are vital for unlocking the full potential of electronic recycling, especially for complex components and devices.
Sustainable Approaches for Digital Devices
Sustainability in the context of digital devices extends beyond just recycling; it encompasses the entire lifecycle, from design to disposal. Innovations in materials science are leading to the development of more eco-friendly components, such as biodegradable plastics or easily separable adhesives, which simplify the recycling process at the end of a device’s life. Furthermore, business models promoting repair, reuse, and refurbishment are gaining traction, extending the lifespan of electronics and reducing the overall volume of waste generated. This holistic approach is essential for fostering a truly circular economy for electronics.
The Future of Electronic Recycling Innovation
Looking ahead, the future of electronic recycling is likely to be shaped by further integration of cutting-edge technologies and a stronger emphasis on circular economy principles. This includes advancements in areas like quantum computing, which could potentially revolutionize material science and enable even more precise and energy-efficient recycling techniques in the long term. Continuous innovation in areas such as flexible electronics and wearable technology also necessitates adaptable recycling solutions that can handle novel materials and designs. The focus will remain on developing scalable, cost-effective, and environmentally sound methods for managing the world’s growing electronic waste.
| Type of Recycling Service/Innovation | Implementation Cost Estimation (Approximate) | Benefits/Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Advanced Mechanical Sorting Facility | €500,000 - €5,000,000+ | Higher purity material recovery, reduced manual labor |
| AI-Powered Material Identification | €100,000 - €1,000,000 (per system) | Increased sorting accuracy, faster processing |
| Chemical Leaching for Precious Metals | €200,000 - €2,000,000+ | High recovery rate for rare metals, reduced environmental footprint |
| Refurbishment & Reuse Programs | €50,000 - €500,000 (startup costs) | Extended product lifespan, reduced new resource demand |
| Nanotechnology-based Extraction | €1,000,000 - €10,000,000+ (R&D/pilot) | Ultra-fine material recovery, neutralization of complex toxins |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
The ongoing pursuit of innovative recycling solutions for electronic waste is a testament to the global commitment towards environmental stewardship and resource efficiency. By embracing advanced technologies, fostering sustainable design principles, and supporting robust recycling infrastructures, societies can transform the challenge of e-waste into an opportunity for economic growth and ecological preservation. These collective efforts are indispensable for building a more sustainable future in an increasingly digitized world.