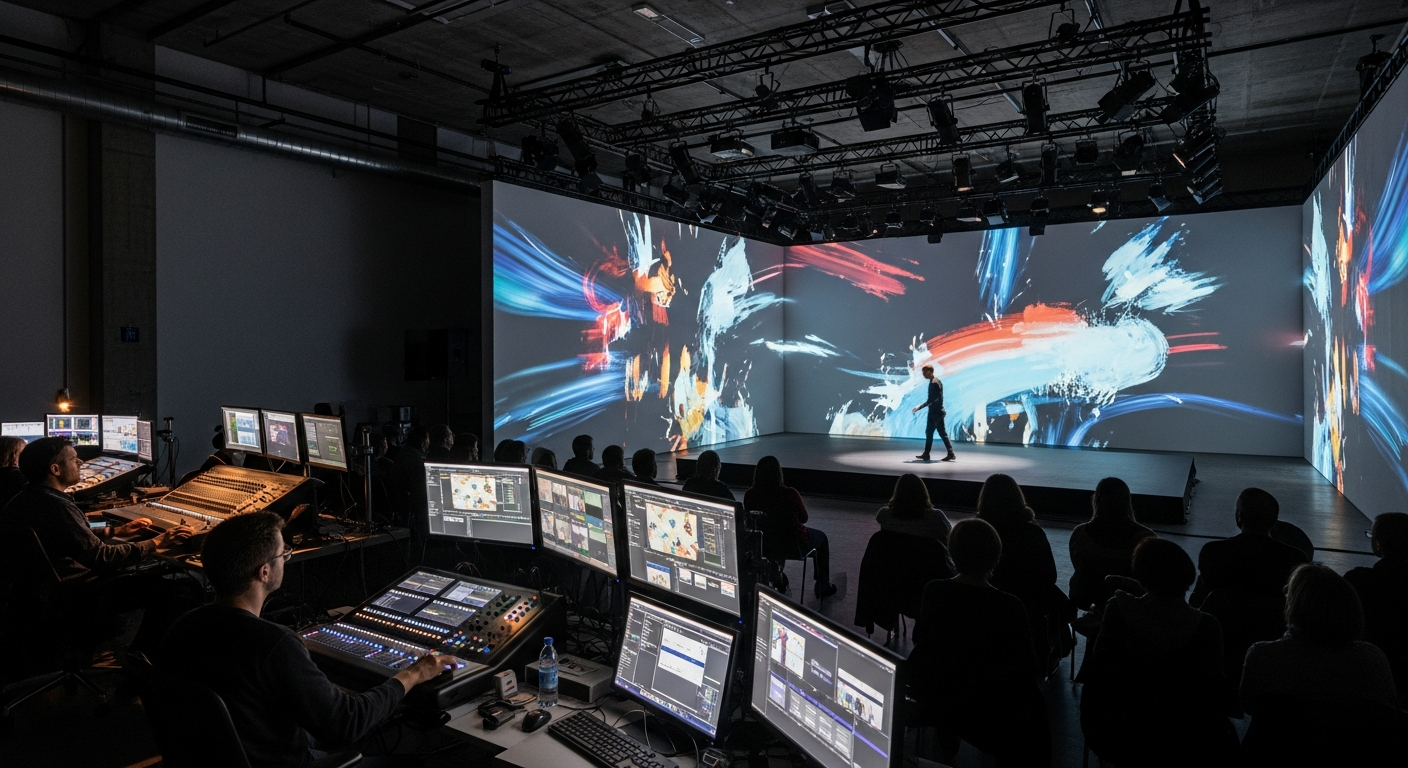
Cultural Movements Influencing Modern Creative Fields
Cultural movements are profound forces that shape societies and, consequently, the creative output within them. From historical shifts like the Renaissance to contemporary digital trends, these movements provide the context, inspiration, and sometimes the very tools through which artists, designers, and storytellers express themselves. Understanding their impact offers insight into the evolution of art forms across various domains, including visual arts, music, literature, and digital media, highlighting how collective human experiences translate into diverse forms of expression and innovation.
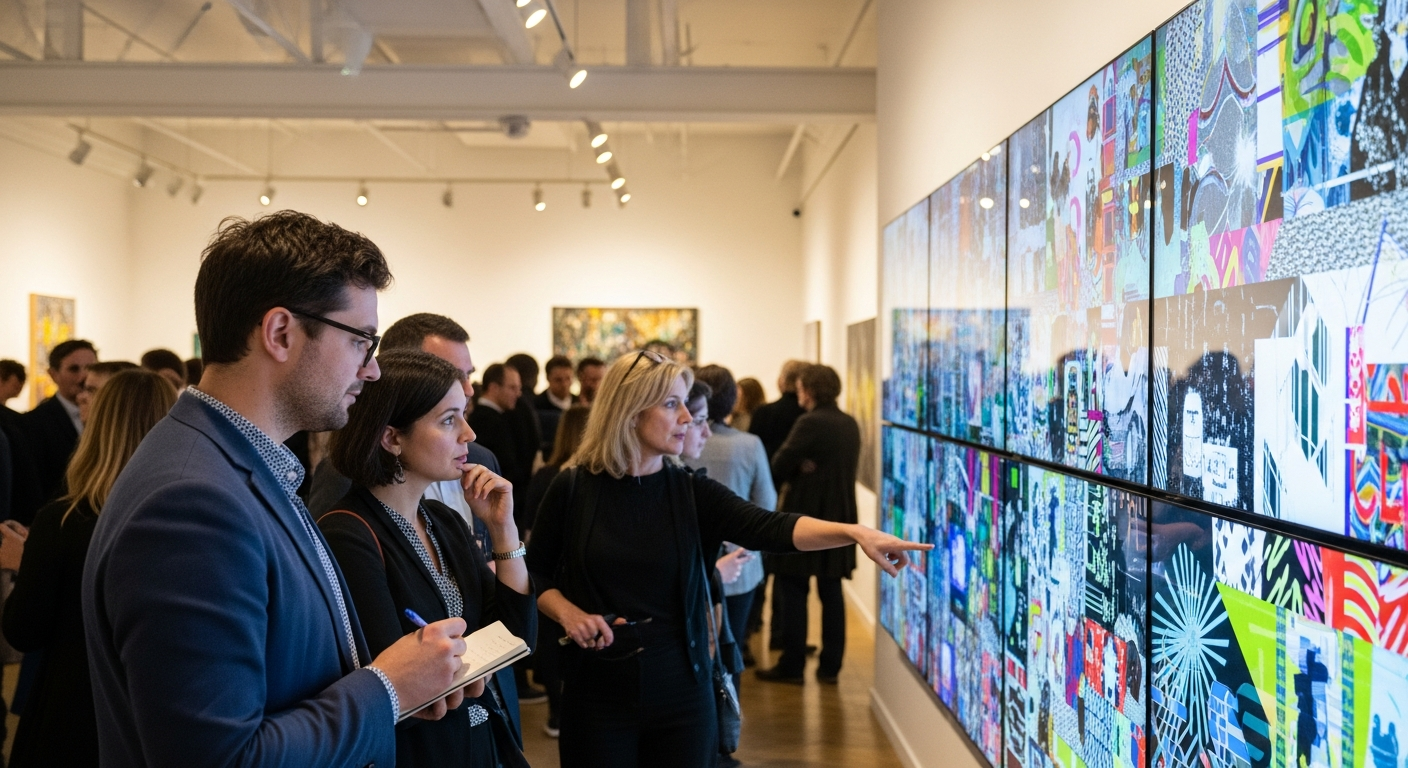

The Evolution of Creativity and Cultural Expression
Cultural movements serve as catalysts for human creativity and expression, reflecting the prevailing philosophies, social structures, and technological advancements of their time. These shifts are not merely aesthetic; they often emerge from significant historical events, political changes, or scientific discoveries, influencing how artists perceive the world and choose to communicate their ideas. The interplay between a society’s values and its artistic output is fundamental, with each feeding into the other to create distinct periods of innovation. This continuous dialogue between culture and creativity ensures that art remains a dynamic and responsive mirror to human experience, constantly evolving with new generations of artists and their audiences.
Historically, movements like Romanticism emphasized emotion and individualism, while Modernism explored abstraction and a break from tradition. These periods fostered unique forms of artistic expression, pushing boundaries in painting, sculpture, and literature. Contemporary artists continue to draw upon and react against these historical precedents, blending traditional techniques with modern sensibilities. The collective consciousness of a culture often dictates the themes, styles, and narratives that resonate most deeply, shaping the very foundation of creative endeavors.
Shaping Visual and Performing Arts
Visual arts, encompassing painting, sculpture, photography, and graphic design, are particularly sensitive to cultural currents. Movements such as Pop Art, born from post-war consumerism, directly incorporated elements of popular culture and commercial imagery, challenging traditional notions of fine art. Similarly, street art and graffiti, often rooted in urban culture and social commentary, have evolved from subversive acts into recognized forms of artistic expression, showcased in galleries and public spaces worldwide. These visual shifts reflect broader societal conversations about identity, consumption, and social justice.
Performance arts, including theatre, dance, and live spectacle, also undergo significant transformations influenced by cultural movements. The avant-garde movements of the early 20th century, for instance, sought to dismantle conventional theatrical structures, promoting experimental forms that engaged audiences in new ways. Modern performance often integrates technology, interdisciplinary approaches, and immersive experiences, reflecting a cultural desire for interactive and multi-sensory engagement. The design elements, from stage sets to costumes, are meticulously crafted to convey specific cultural narratives or challenge established norms, making each performance a reflection of its contemporary context.
Narrative Forms: Literature, Cinema, and Media
Literature, cinema, and various forms of media are powerful vehicles for narrative and storytelling, continuously shaped by cultural shifts. Literary genres, from epic poetry to the modern novel, reflect the changing human condition and societal concerns. Postmodern literature, for example, often deconstructs traditional narrative structures and questions grand narratives, mirroring a cultural skepticism towards universal truths. This approach has influenced how stories are told and consumed, emphasizing subjectivity and multiple perspectives.
Cinema, as a relatively young art form, has rapidly evolved alongside cultural and technological advancements. Neorealism in post-war Italy captured the harsh realities of everyday life, while the French New Wave experimented with narrative and editing techniques, challenging Hollywood conventions. Today, digital media platforms and streaming services have revolutionized how films and series are produced and distributed, leading to an explosion of diverse genres and narratives that cater to a global audience. The industry constantly adapts to cultural demands for representation, authenticity, and innovative storytelling, influencing how stories are consumed and interpreted across different cultures.
The Influence of Digital Culture
The rise of digital culture represents one of the most significant cultural movements of the past few decades, profoundly impacting nearly every creative field. Digital technologies have democratized access to tools and platforms, enabling a broader range of artists to create and share their work. From digital painting and animation to virtual reality experiences and interactive installations, the expressive possibilities have expanded dramatically. This shift has also fostered new forms of collaboration and community among artists, transcending geographical boundaries.
Furthermore, digital culture has altered the relationship between creators and their audience. Social media platforms, online galleries, and streaming services provide direct channels for artists to connect with their followers, receive feedback, and even fund their projects. This direct engagement has led to the emergence of new industry models and distribution strategies, challenging traditional gatekeepers. The speed at which digital trends evolve means that creative fields are in a constant state of adaptation, incorporating new technologies and engaging with internet-native forms of expression.
Music’s Dynamic Landscape and Audience Engagement
Music, being inherently tied to cultural identity and social ritual, consistently reflects and drives cultural movements. From the protest songs of the folk revival to the diverse genres born from urban experiences like hip-hop and electronic dance music, musical styles embody specific cultural moments and sentiments. Each genre carries its own set of aesthetic principles, lyrical themes, and performance practices, often becoming a voice for particular communities or ideologies. The evolution of music is a testament to cultural exchange and innovation, with global influences continually shaping local sounds.
Technological advancements have also dramatically influenced music production, distribution, and audience engagement. Recording technologies allowed for the mass dissemination of music, while digital tools have made music creation more accessible. The shift from physical media to streaming services has transformed how music is consumed, leading to personalized playlists and global discoverability. This dynamic landscape encourages artists to experiment with different genres and collaborate across cultural lines, fostering a rich tapestry of musical expression that resonates with a diverse international audience.
Craft, Innovation, and Industry Dynamics
The concept of craft within creative fields has also been redefined by cultural movements and technological innovation. While traditional crafts emphasize manual skill and heritage, modern craft often incorporates digital fabrication, sustainable practices, and interdisciplinary approaches. This blending of old and new reflects a cultural appreciation for both artisanal quality and forward-thinking design. The industry surrounding creative fields is constantly adapting to these shifts, from the business models of art galleries and publishing houses to the organizational structures of film studios and music labels.
The creative industries are driven by a continuous need for innovation, responding to changing consumer tastes, technological capabilities, and cultural narratives. This dynamic environment fosters a competitive landscape where artists and creators must not only hone their craft but also understand the broader industry context. The interplay between individual artistic vision and the commercial demands of the market shapes what art is produced, how it is distributed, and ultimately, how it influences and is influenced by the cultural landscape.
Cultural movements are integral to the ongoing evolution of creative fields, providing both the impetus and the framework for artistic innovation. From the subtle shifts in aesthetic preference to revolutionary changes in how art is created and consumed, these movements underscore the deep connection between human society and its expressive output. By understanding these influences, we gain a richer appreciation for the diverse forms of creativity that define our modern world, recognizing art as a continuous dialogue between past traditions and future possibilities.