Adapting Eating Habits to a Changing Global Climate
The global climate is undergoing significant changes, profoundly impacting the agricultural systems that sustain our food supply. From shifting weather patterns to altered growing seasons, these environmental transformations necessitate a reevaluation of our food choices and consumption habits. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for fostering more resilient food systems and ensuring future food security, prompting a broader discussion on how our daily plates will evolve.
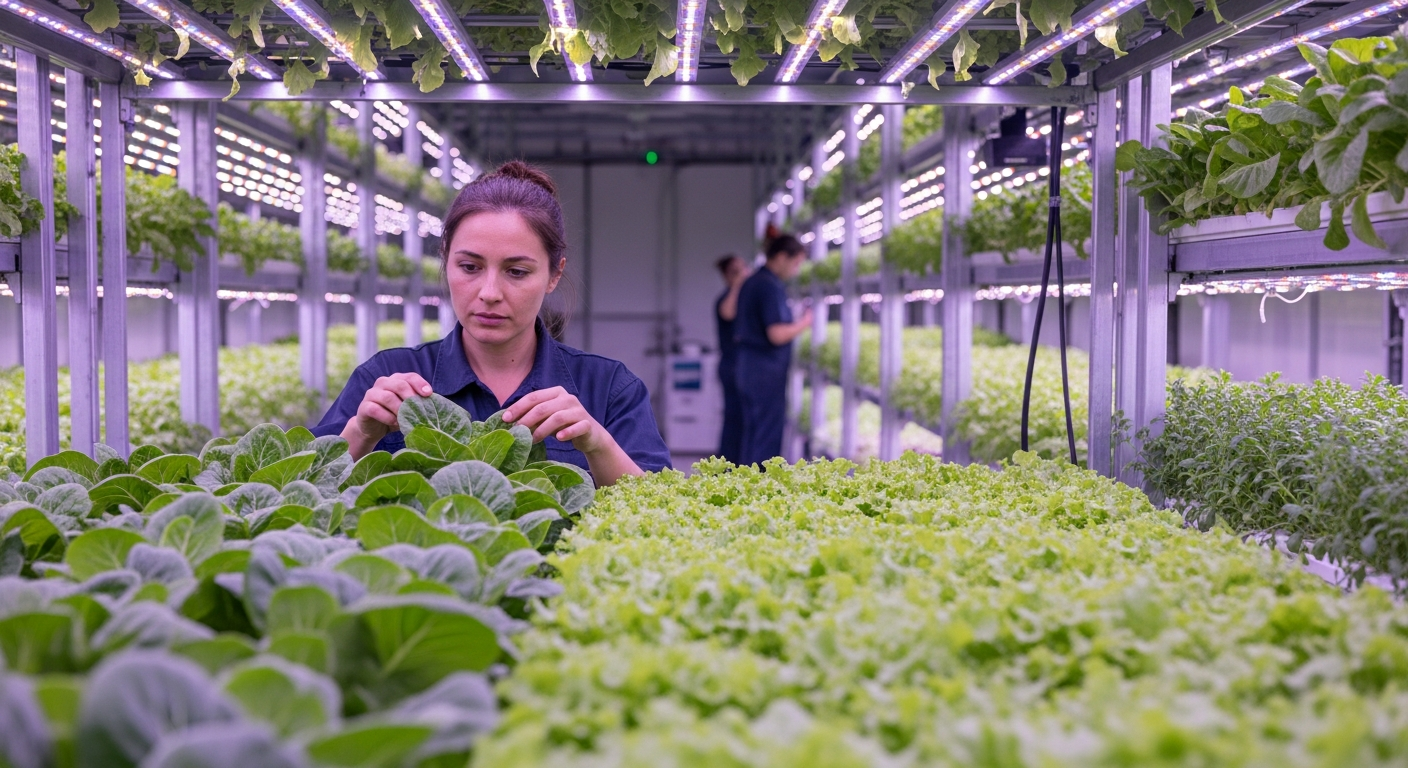

The global climate is experiencing unprecedented shifts, presenting challenges to how food is produced, distributed, and consumed worldwide. These changes are not merely theoretical; they are already influencing crop yields, the availability of certain ingredients, and the economic viability of traditional farming practices across diverse regions. Adapting to these new realities requires a comprehensive approach, encompassing everything from agricultural innovation to individual dietary adjustments.
The Impact of Climate Change on Global Agriculture and Produce
Climate change significantly alters the landscape of global agriculture and the availability of produce. Rising temperatures, altered precipitation patterns, and an increase in extreme weather events such as droughts and floods directly affect crop growth cycles, soil health, and water resources. This can lead to reduced yields for staple foods, shifts in the geographical areas suitable for cultivating specific ingredients, and an increased vulnerability to pests and diseases. Understanding these impacts is the first step toward developing resilient agricultural practices that can withstand future environmental pressures and ensure a consistent supply of nutritious food globally.
Shifting Culinary Traditions and Ingredient Sourcing
As environmental conditions change, so too will the availability of traditional ingredients, prompting shifts in culinary traditions and ingredient sourcing. Many beloved cuisines are deeply rooted in local produce and specific environmental conditions. When these conditions change, cooks and gastronomes may need to explore alternative ingredients or adapt classic recipes. This could lead to a greater emphasis on local and seasonal sourcing, promoting biodiversity, and fostering the cultivation of more climate-resilient crops. The challenge lies in maintaining the integrity and flavors of diverse culinary heritage while embracing new approaches to food preparation and dining.
Embracing Sustainable Nutrition and Wellness Trends
Adapting eating habits to a changing climate naturally aligns with the growing emphasis on sustainable nutrition and wellness trends. Diets that prioritize plant-based foods, reduce meat consumption, and minimize food waste are often more environmentally friendly and can offer significant health benefits. Focusing on nutrition derived from a diverse range of plant sources, including legumes, grains, and various fruits and vegetables, can enhance dietary health while simultaneously reducing the carbon footprint associated with food production. This shift contributes to both individual wellness and broader ecological sustainability.
Exploring New Flavors, Tastes, and Dining Cultures
The evolution of our food systems in response to climate change also presents an opportunity to explore new flavors, tastes, and dining cultures. As certain ingredients become less available, or new climate-adapted crops emerge, chefs and home cooks alike will experiment with novel combinations and preparations. This innovative approach to gastronomy can lead to the discovery of exciting new culinary experiences, expanding our palates and enriching the global food landscape. It encourages a dynamic reinterpretation of what it means to dine well, fostering creativity and adaptability within the food community.
The Role of Beverages and Conscious Consumption
Beverages are an integral part of global food culture, and their production is also susceptible to climate change. Crops like coffee beans, tea leaves, and grapes for wine are highly sensitive to specific climatic conditions. Changes in temperature and rainfall can affect their quality, yield, and even the regions where they can be grown. This necessitates a focus on conscious consumption, encouraging consumers to consider the environmental impact of their beverage choices. Supporting sustainable farming practices for beverages, exploring locally sourced options, and reducing overall consumption can contribute to a more resilient and responsible approach to what we drink.
Adapting eating habits to a changing global climate is a multifaceted endeavor that touches upon agriculture, culinary arts, nutrition, and cultural practices. It involves a conscious effort to understand environmental impacts, embrace sustainable sourcing, and foster innovation in how we approach food. By making informed choices and supporting resilient food systems, individuals and communities can contribute to a more sustainable future for global food and gastronomy.